Batteries are an essential part of our daily lives, powering everything from remote controls and smoke detectors to smartphones and electric vehicles. Despite their ubiquity, many of us are storing batteries incorrectly, leading to reduced lifespan, potential hazards, and unnecessary waste. Proper battery storage is crucial for maintaining their performance and ensuring safety.
In this article, we will explore the science behind battery storage and debunk common myths that have led us astray. By understanding the right techniques, you can extend the life of your batteries, save money, and contribute to a healthier environment. Let’s delve into the details and discover how to store your batteries the right way.
1. Understanding Battery Chemistry and Why It Matters
Different types of batteries, such as alkaline, lithium-ion, and nickel-metal hydride, have distinct chemical compositions that affect their performance and storage needs. Alkaline batteries, commonly used in household items, have a zinc and manganese dioxide composition, while lithium-ion batteries, found in electronics, use lithium compounds as electrodes.
The chemical reactions within these batteries are sensitive to temperature, humidity, and even the way they are stored. For example, lithium-ion batteries degrade faster when exposed to temperatures above 30°C (86°F), whereas alkaline batteries can leak if stored in high humidity. Understanding these differences helps in developing an effective storage strategy.
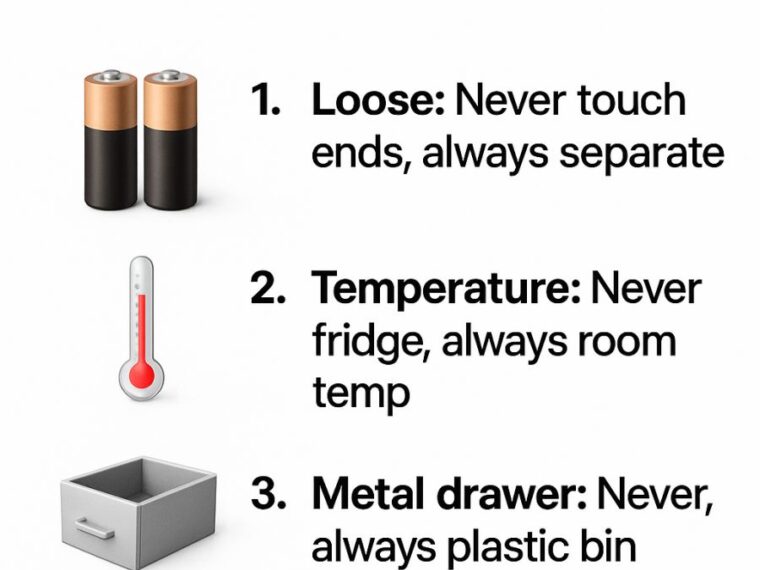
2. The Importance of Keeping Battery Ends Separated
Battery ends, or terminals, are the points of electrical contact where energy is transferred. If the positive and negative terminals touch, they can short-circuit, leading to overheating or even a fire.
To prevent accidental contact, store batteries in their original packaging or use a battery storage case where each battery is fitted snugly into its slot. This is especially important for 9-volt batteries, which have terminals close together, increasing the risk of short-circuits.
3. Why Room Temperature Is the Ideal Storage Condition
Room temperature, typically around 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F), is ideal for battery storage. At this range, the chemical reactions within the battery are stable, minimizing self-discharge and preserving capacity.
Storing batteries in extreme temperatures, either too hot or too cold, can lead to reduced efficiency and a shorter lifespan. For instance, at temperatures below 0°C (32°F), alkaline batteries lose capacity, while lithium-ion batteries may suffer from permanent capacity loss if exposed to temperatures above 30°C (86°F) for extended periods.
4. Avoiding Metal: The Case for Plastic Storage Bins
Storing batteries in metal containers can create a risk of short-circuiting if the terminals come into contact with the metal. Plastic storage bins provide a non-conductive environment, reducing this risk.
Use plastic bins with dividers to keep batteries organized and separated by type and size. This not only prevents contact between terminals but also helps in quickly finding the right battery when needed.
5. The Risks of Storing Batteries in the Refrigerator
One common myth is that storing batteries in the refrigerator extends their life. While cooler temperatures can slow down the self-discharge rate, the high humidity inside a refrigerator can lead to condensation, which can cause corrosion and damage the battery.
Instead of refrigerating, store batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and heat sources. Ensuring the environment is stable will help maintain the integrity of your batteries.
6. How to Identify and Properly Recycle Expired Batteries
Expired batteries often show signs of leakage, corrosion, or a swollen appearance. These indicators mean the battery’s chemicals have degraded and it’s no longer safe to use.
Proper disposal is essential for environmental safety. Many local waste management facilities offer battery recycling programs. Look for designated drop-off points in your area, and never dispose of batteries in regular trash as they can leak harmful chemicals into the environment.
7. The Dangers of Mixing Different Battery Types
Mixing different types of batteries, such as alkaline with lithium, in a device can lead to uneven discharge rates and potential leakage. Different chemistries have varied discharge curves and voltages, which can cause one battery to over-discharge while the other remains charged, increasing the risk of leakage.
Always use the same type and brand of batteries in a device to ensure consistent performance and reduce the risk of damage.
8. The Benefits of Using Original Packaging
The original packaging is designed to protect batteries from external elements like humidity and dust, and to prevent short-circuits by isolating the terminals.
Keeping batteries in their original packaging until use ensures they remain in optimal condition. It also helps in organizing and identifying battery types and expiration dates, facilitating timely use and replacement.
9. Tips for Storing Rechargeable Batteries Safely
Rechargeable batteries, such as nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) and lithium-ion, require specific care. Store them at a 40-60% charge level to reduce stress on the battery and prolong its life.
Avoid storing rechargeable batteries fully charged or fully depleted, as this can affect their capacity over time. Keep them in a cool, dry place, and regularly check their charge level if stored for long periods.
10. Common Myths About Battery Storage Debunked
Several myths about battery storage persist, such as the belief that refrigerating batteries extends their life or that fully discharging them before recharging is beneficial.
In reality, modern batteries are designed to perform optimally without such practices. Refrigeration poses more risks than benefits, and fully discharging can harm rechargeable lithium-ion cells. Understanding these myths and the facts behind them helps in making informed storage decisions.
11. Viral Hacks: What Works and What Doesn’t in Battery Storage
Social media is rife with battery storage hacks, some of which are effective while others are not. For example, using silica gel packets to keep batteries dry is a useful tip, as they absorb moisture and reduce the risk of corrosion.
On the other hand, storing batteries in the freezer, a common viral hack, does more harm than good due to potential condensation issues. Always verify hacks with scientific backing before trying them, to ensure the safety and longevity of your batteries.