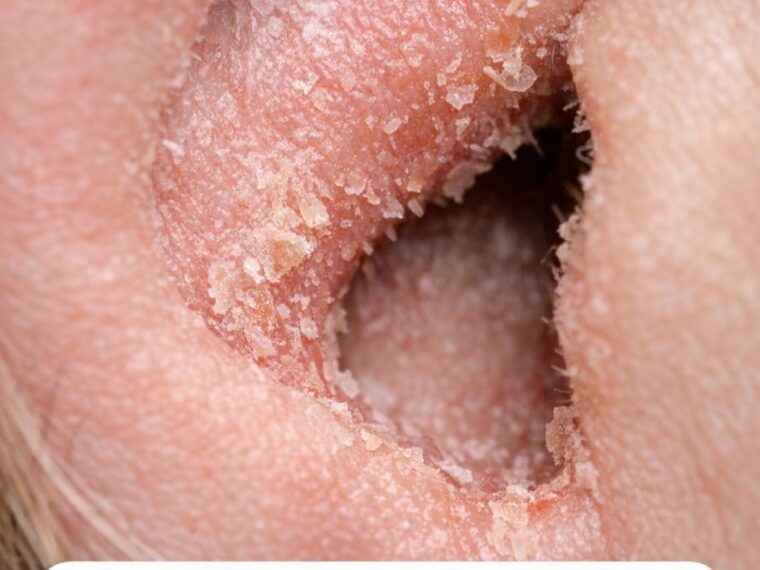
Itching and flaking skin inside and around the ears can be an uncomfortable and annoying problem, especially during the colder months. This common complaint can arise from a variety of causes, and understanding the underlying factors is crucial for effective relief. Many people experience this issue more intensely in winter, when environmental conditions exacerbate skin dryness and irritation.
In this article, we will explore the potential reasons behind itchy, flaky ear skin, focusing on seasonal influences and other contributing factors. From environmental conditions to underlying dermatological conditions, we will delve into the science and provide practical advice for managing and alleviating symptoms.
1. Winter Air: How Cold, Dry Weather Strips Moisture From Delicate Ear Skin
During winter, the air is often cold and dry, which can significantly impact the skin’s ability to retain moisture. Humidity levels tend to drop below 30% in colder climates, leading to increased evaporation of moisture from the skin’s surface. The delicate skin inside and around the ears is particularly susceptible to this moisture loss, resulting in dryness and flakiness.
Cold weather also causes blood vessels to constrict, reducing blood flow to the skin and hindering the delivery of essential nutrients and hydration. This can lead to a compromised skin barrier, making it more prone to irritation and itching. Protective measures like using a humidifier indoors and applying rich moisturizers can help mitigate these effects.
2. Ear Canal Dermatitis: When Your Ear’s Lining Becomes Inflamed and Angry
Ear canal dermatitis is an inflammatory condition affecting the lining of the ear canal. It can be triggered by allergens, irritants, or infections, and often presents with redness, itching, and flaking of the skin. The ear canal’s narrow structure and limited ventilation create an environment where moisture and irritants can easily become trapped, exacerbating symptoms.
Managing ear canal dermatitis involves identifying and avoiding potential triggers, such as harsh shampoos or ear cleaning tools, and using medicated drops or creams prescribed by a healthcare provider to reduce inflammation.
3. Eczema and Psoriasis: Common Skin Conditions That Target the Ears
Eczema and psoriasis are chronic skin conditions that can affect the ears, causing itchiness, redness, and flaking. Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, often occurs in people with a family history of allergies and asthma. It can cause intense itching and the formation of dry, scaly patches.
Psoriasis, on the other hand, is an autoimmune condition that leads to the rapid turnover of skin cells, resulting in the buildup of thick, silvery scales. Both conditions require specialized treatment plans, often involving topical corticosteroids and moisturizers to manage flare-ups and maintain skin hydration.
4. Contact Allergies: Earrings, Hair Products, and Headphones as Hidden Triggers
Contact allergies occur when the skin reacts to substances it comes into contact with, leading to localized itching and irritation. Common culprits around the ears include nickel in earrings, fragrances or preservatives in hair products, and materials in headphones or ear cushions.
Identifying the allergen is key to preventing future reactions. Patch testing by a dermatologist can help pinpoint specific allergens, allowing individuals to choose hypoallergenic alternatives and avoid exposure.
5. Overcleaning With Cotton Swabs: Why Digging for Wax Makes Itching Worse
While it may be tempting to use cotton swabs to clean the ears, this practice can actually worsen itching and irritation. Cotton swabs can push earwax deeper into the canal, potentially causing blockages and irritation.
Moreover, overcleaning strips the ear of its natural oils, leading to dryness and increased sensitivity. It is generally recommended to let the ears self-clean and to only remove visible wax with a damp cloth.
6. Earbuds, Headsets, and Hearing Aids: Friction, Sweat, and Micro-Irritation
Frequent use of earbuds, headsets, or hearing aids can lead to friction and pressure on the ear’s skin, resulting in micro-irritations. These devices can also trap sweat and moisture, creating an ideal environment for irritation and infection.
To minimize these effects, users should ensure proper fit and hygiene of devices, allowing the ears to breathe and cleaning the devices regularly to prevent the buildup of bacteria and debris.
7. Seborrheic Dermatitis: The Same Flaky Skin From Your Scalp, Now in Your Ears
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by red, scaly patches. It commonly affects areas rich in sebaceous glands, including the scalp and the ears. This condition is often associated with an overgrowth of a yeast called Malassezia, which thrives in oily environments.
Treatment typically involves antifungal shampoos or creams to reduce yeast proliferation, along with anti-inflammatory treatments to soothe the skin and reduce scaling.
8. Viral “Cure-All” Hacks: Oils, Hydrogen Peroxide, and Other TikTok Trends to Avoid
Social media platforms like TikTok have popularized various ‘cure-all’ hacks for ear problems, including using oils or hydrogen peroxide to clean ears or alleviate itching. However, many of these methods lack scientific backing and can potentially harm the delicate ear skin.
Oils can create a breeding ground for bacteria, while hydrogen peroxide can irritate and dry out the skin further. It is crucial to approach such trends with skepticism and consult with healthcare professionals before trying new remedies.
9. Safe At-Home Relief: Gentle Cleansing, Moisturizing, and Barrier Repair for Ear Skin
For safe at-home relief of itchy, flaky ear skin, gentle cleansing and moisturizing are essential. Use mild, fragrance-free cleansers to avoid further irritation and apply hypoallergenic moisturizers to restore the skin’s barrier function.
Products containing ceramides or hyaluronic acid can be particularly effective in providing hydration and supporting the skin’s natural repair processes. Creating a consistent skincare routine can help maintain healthy ear skin, especially during the harsh winter months.
10. When It’s an Infection: Recognizing Yeast or Bacterial Overgrowth in the Ear
Infections in the ear can develop when bacteria or yeast multiply excessively, often due to trapped moisture or breaks in the skin barrier. Symptoms can include increased redness, pain, swelling, and discharge.
Medical evaluation is necessary to identify the type of infection and prescribe appropriate treatments, such as antifungal or antibiotic medications. Keeping the ears dry and clean is crucial in preventing recurrent infections.
11. When to See a Doctor: Red-Flag Symptoms and What an ENT or Dermatologist Can Do
While many causes of itchy, flaky ear skin can be managed at home, certain symptoms warrant medical attention. These include severe pain, persistent discharge, hearing loss, or symptoms that do not improve with initial treatment.
An ENT (ear, nose, and throat specialist) or dermatologist can provide a thorough evaluation, conduct tests to diagnose underlying conditions, and offer advanced treatment options to address the root cause of the problem.